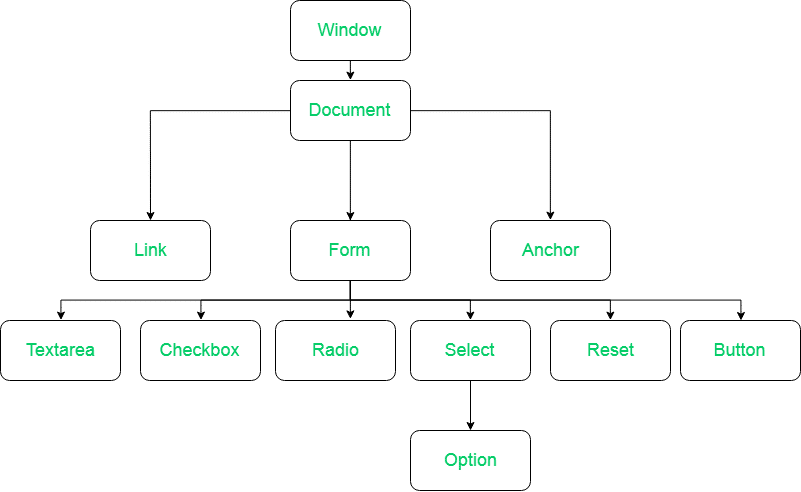
When a web page is loaded in a browser, the browser parses the HTML code and creates a hierarchical representation of the elements present in the page. This hierarchical representation is known as the DOM tree. Each HTML element (e.g., <div>, <p>, <a>, etc.) in the page becomes a node in the DOM tree, and attributes and text content are represented as properties of those nodes.
this is answer from application
this is answer from application
answer



